Available in your clinic
Not available in your clinic
Face treatments
Body treatments
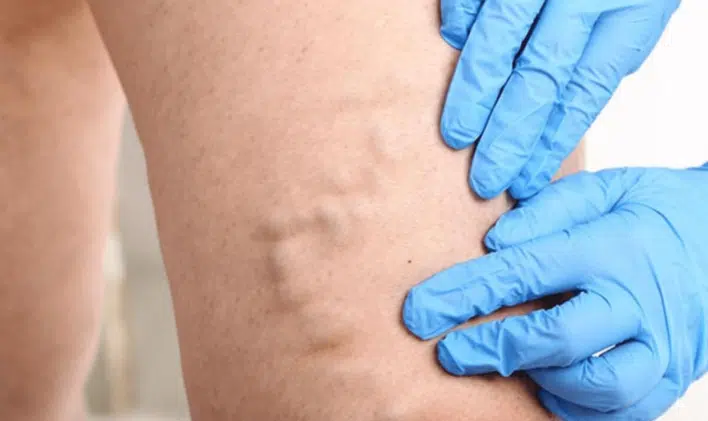
Varicose veins, also called varicosities, are enlarged, twisted, and bluish veins visible beneath the skin. They result from impaired blood circulation caused by weakened vein walls or damaged one-way valves. Commonly appearing on the legs, 95% of cases involve the superficial venous network, primarily the saphenous veins, which transport blood from the feet to the heart. This circulatory dysfunction leads to blood pooling in the affected veins, causing symptoms like pain, a heavy feeling, mild swelling, or warmth in the legs.
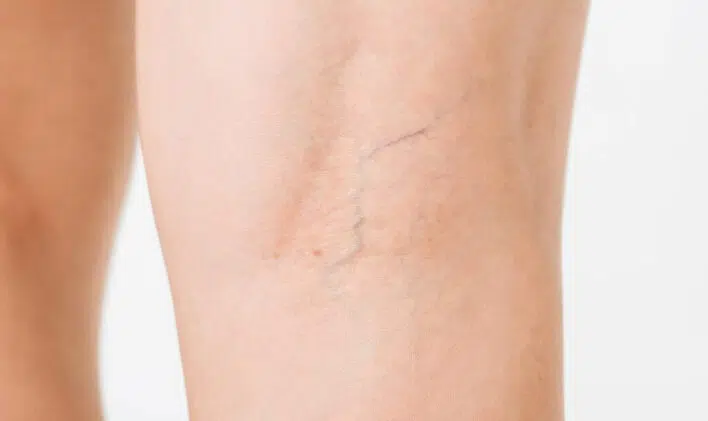
Varicose veins, sometimes referred to as spider veins when smaller or thinner, may also manifest as reticular veins, forming visible filaments under the skin in a tree-branch or web-like pattern. These abnormal veins, also known as telangiectasia, are often accompanied by itching, muscle cramps, and localized swelling (edema).
If left untreated, these dysfunctional veins can lead to complications such as superficial thrombophlebitis, skin ulcers caused by venous insufficiency, or even deep vein thrombosis (DVT), where blood clots form in deeper veins. These clots can obstruct blood vessels, leading to more severe risks like pulmonary embolism, a potentially life-threatening condition.
The primary cause of varicose veins is chronic venous insufficiency, a condition where the venous system, due to weakened valves or vein walls, fails to effectively return blood to the heart. This dysfunction allows blood to pool in the leg veins, often resulting in swollen veins, abnormal blood flow, and the permanent dilation of veins. Gravity exacerbates this issue, particularly in the lower limbs, leading to symptoms such as leg swelling and a heavy feeling. While this condition primarily affects superficial veins, it can also involve deeper veins in advanced cases, increasing the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Venous stasis—a condition where blood pools or stagnates—elevates pressure on the walls of blood vessels, fostering the development of twisted, enlarged varicose veins in the legs and sometimes extending to the ankles. Dysfunctional veins, often within the saphenous venous network, represent a clear disruption in blood circulation. Factors such as prolonged periods of standing, wearing high heels that hinder calf muscle function, or a sedentary lifestyle with insufficient physical activity can make the condition worse, weakening veins and promoting further venous insufficiency.
Other contributing factors include:
Over time, vein walls can lose their elasticity and muscle tone, diminishing their ability to support efficient blood circulation. This weakening impacts the functionality of one-way valves designed to prevent blood from flowing backward. When these valves become damaged or fail, blood pools in the veins, leading to venous insufficiency and contributing to the development of varicose veins and spider veins. This stagnation of blood flow increases pressure within the affected blood vessels, promoting further dilation and the appearance of swollen veins or other visible signs, such as bluish or purple veins.
The leg muscles, particularly the calf muscles, are essential in driving venous blood back to the heart through a process often referred to as the “calf muscle pump.” This mechanism relies on the contraction of these muscles to counteract gravity and maintain proper blood flow. When muscle tone is insufficient—often due to a lack of physical activity, prolonged sitting, or other sedentary habits—the efficiency of this natural pump decreases. This leads to increased venous pressure, promoting the dilation of superficial veins and contributing to conditions such as varicose veins and venous insufficiency. Over time, this can exacerbate symptoms like leg swelling, heaviness, or visible swollen veins.
Prolonged standing or sitting disrupts blood flow in the lower limbs, leading to venous stasis—a condition where blood pools in the veins instead of circulating efficiently. This stagnation, compounded by inactivity or lack of calf muscle movement, increases pressure on vein walls and raises the risk of developing both superficial varicose veins and more serious conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Over time, this can lead to symptoms such as swollen veins, leg swelling, and visible twisted veins in the affected areas.
During pregnancy, the growing uterus exerts pressure on pelvic veins and leg veins, significantly impeding venous return and causing blood to pool in the lower limbs. This increased venous pressure, combined with hormonal changes that weaken vein walls and affect the function of one-way valves, can result in the development of new varicose veins or spider veins, particularly on the legs and ankles. The risk of swollen veins, venous insufficiency, and related symptoms like leg swelling or a heavy feeling is also heightened during this time.
Engage in physical activities that activate leg muscles, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, to boost venous circulation and prevent venous stasis. These exercises promote calf muscle movement, enhance muscle tone, and apply gentle pressure to the veins, which is crucial for maintaining proper blood flow and supporting venous return to the heart. Regular exercise also helps reduce the risk of developing varicose veins, spider veins, and other complications related to venous insufficiency.
A fiber-rich diet combined with low salt intake helps minimize water retention, reduce leg swelling, and decrease pressure on vein walls, all of which are beneficial for maintaining healthy blood vessels and preventing varicose veins. Incorporating antioxidant-rich foods like berries, citrus fruits, and leafy greens can further strengthen vein walls and support blood circulation, reducing the risk of venous insufficiency, spider veins, and other related conditions.
Excess weight exerts additional pressure on leg veins, compromising their function and elevating the risk of dilated veins or incompetent veins. This added venous pressure not only weakens vein walls but also impairs the efficiency of one-way valves, leading to blood pooling and contributing to venous insufficiency, varicose veins, and spider veins. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet is essential to reduce strain on blood vessels and support proper blood flow and venous return.
Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing, as these positions can restrict blood flow and contribute to venous stasis. Instead, incorporate regular movement into your routine to stimulate leg muscles and enhance venous circulation. Elevating your legs above heart level periodically helps reduce venous pressure, prevent blood pooling, and support venous return. These practices are essential for minimizing the risk of varicose veins, spider veins, leg swelling, and other complications associated with venous insufficiency.
Wearing loose clothing, especially around the legs, helps prevent compression of blood vessels, ensuring healthy blood flow and reducing the risk of venous insufficiency. Tight garments can exacerbate issues like blood pooling and swollen veins, particularly in individuals prone to varicose veins or spider veins. Additionally, avoiding high heels is crucial, as they alter posture and reduce the efficiency of the calf muscle pump, which plays a vital role in returning venous blood to the heart. Opting for comfortable footwear supports proper leg muscle function and promotes overall venous circulation.
Avoid hot baths, saunas, or prolonged exposure to excessive heat, as these can cause vein dilation and worsen venous insufficiency by increasing venous pressure and promoting blood pooling. Such conditions may contribute to the development of varicose veins, spider veins, and other circulatory issues. Instead, opt for lukewarm showers, which help maintain proper blood circulation, support vein wall integrity, and reduce the risk of complications like leg swelling or swollen veins.
Compression garments, such as compression stockings or compression bandages, apply graduated pressure to the legs, promoting venous circulation and enhancing blood flow back to the heart. This gentle yet effective pressure helps reduce symptoms like a heavy feeling, leg swelling, and mild pain. These garments are particularly beneficial for preventing the development of new varicose veins, spider veins, or other complications associated with venous insufficiency, especially in at-risk individuals such as those with prolonged standing or sitting habits, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) history, or weakened valves. Regular use of compression therapy can also support recovery after varicose vein treatment or surgical procedures.
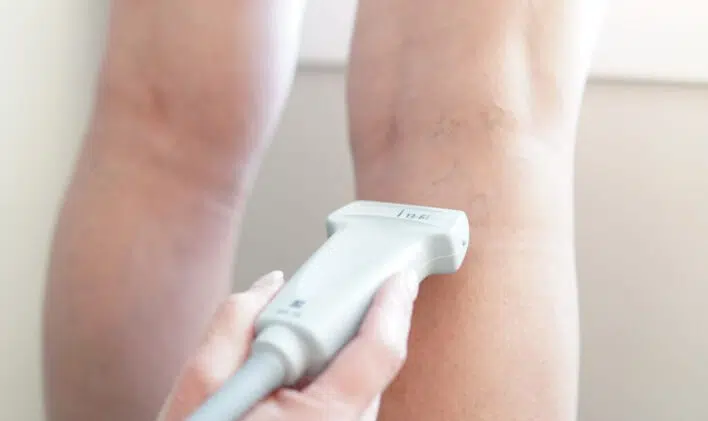
Sclerotherapy treatment for varicose veins and superficial veins is minimally invasive and requires no recovery time, making it a convenient option. A healthcare provider injects a sclerosant solution into the abnormal vein, causing it to seal and redirect blood flow to healthier blood vessels, enhancing venous circulation.
Depending on the size and extent of the condition, multiple sessions may be required. For long-term success, follow-up treatments are often necessary to prevent new varicosities or spider veins. A healthcare provider will perform a comprehensive evaluation, including a physical examination, to assess deep veins and risk factors, ensuring safe and effective management of venous insufficiency.

Guided by sound waves, a healthcare provider injects a sclerosant solution with precision, sealing the damaged vein and redirecting blood flow to healthier vessels.
Ideal for cases of chronic venous insufficiency or complex conditions, it minimizes risks and provides excellent results. A healthcare provider will evaluate your deep veins and create a personalized plan tailored to your needs.
Known as endovenous laser treatment (EVLT) or laser vein surgery, this procedure is a modern alternative to traditional vein surgery. A healthcare provider inserts a laser fiber into a catheter within the problematic vein. The laser energy destroys the vein walls, which are absorbed by the body, improving blood flow and venous circulation.
Particularly effective for deep varicose veins, this treatment reduces risks like venous insufficiency or blood clots. A healthcare provider may recommend endovenous ablation or alternative treatments based on a thorough assessment.
The VenaSeal technique uses a medical adhesive applied by a healthcare provider through a small catheter to seal the vein, redirecting blood flow to healthier vessels. Unlike other treatments, VenaSeal requires no anesthesia, medication, or compression stockings, offering a convenient, patient-friendly solution.
A healthcare provider will evaluate whether VenaSeal, endovenous ablation, or another treatment like sclerotherapy is the best choice, based on your symptoms and medical history.

Shop our products for an enhanced beauty routine!
Dermapure is Canada’s largest network of premium medical aesthetic clinics, renowned for its exceptional medical team and dedication to helping clients achieve their aesthetic goals. With locations nationwide, Dermapure offers advanced treatments and personalized care, setting the standard for excellence in medical aesthetics.
Subscribe to our newsletter get $25 off your first purchase*
Welcome! Longevity Medical is now Dermapure Parksville!
Our commitment remains unwavering. Same clinics, doctors, and staff. Step in with confidence; your well-being is our constant dedication.
Welcome! Dermal Laser Centres is now Dermapure!
Our commitment remains unwavering. Same clinics, doctors, and staff. Step in with confidence; your well-being is our constant dedication.
Welcome! ReNue clinic is now Dermapure!
Our commitment remains unwavering. Same clinics, doctors, and staff. Step in with confidence; your well-being is our constant dedication
Welcome! Rosenthal Clinic is now
Dermapure Victoria
Our commitment remains unwavering. Same clinics, doctors, and staff. Step in with confidence; your well-being is our constant dedication
Welcome! Skinposible is now
Dermapure Calgary Chaparral
Our commitment remains unwavering. Same clinics, doctors, and staff. Step in with confidence; your well-being is our constant dedication
Welcome! Viva Medical Aesthetics is now
Dermapure Cowichan!
Our commitment remains unwavering. Same clinics, doctors, and staff. Step in with confidence; your well-being is our constant dedication
Welcome! Dr. Boulous Medical Spa is now
Dermapure Newmarket!
Our commitment remains unwavering. Same clinics, doctors, and staff. Step in with confidence; your well-being is our constant dedication
Welcome! Peause is now
Dermapure Longueuil-sur-le-parc
Our commitment remains unwavering. Same clinics, doctors, and staff. Step in with confidence; your well-being is our constant dedication
Welcome! Bellissima Medical is now
Dermapure Dieppe!
Our commitment remains unwavering. Same clinics, doctors, and staff. Step in with confidence; your well-being is our constant dedication
Welcome! RevitalizeMD is now
Dermapure West Edmonton!
Our commitment remains unwavering. Same clinics, doctors, and staff. Step in with confidence; your well-being is our constant dedication